Are you struggling with persistent lower back pain? You’re not alone. Lower back pain is a common health issue. The good news is that targeted exercises can provide significant relief. The key to managing lower back pain lies in a combination of stretching and strengthening exercises. Whether you have muscle strain, herniated discs, or sciatica, the right routine can make a remarkable difference.
In this comprehensive guide, we’ll explore expert-approved exercises that effectively target lower back pain. From gentle stretches to core-strengthening movements, you’ll find a step-by-step approach to rehabilitation. This approach is backed by physical therapy expertise. Let’s dive into these proven exercises that can help you regain mobility, reduce discomfort, and prevent future back problems.
Key Takeaways:
- Lower back pain is common and affects daily activities. It can be managed through proper exercise and stretching routines.
- A combination of gentle stretches and core-strengthening exercises forms the foundation of an effective rehabilitation program.
- Regular exercise and proper stretching techniques are crucial for immediate pain relief and long-term prevention.
- Physical therapy-approved exercises can address various conditions, supporting a gradual return to normal activities.
- The right program should strengthen abdominal muscles and improve spinal stability while maintaining proper form.
Understanding Lower Back Pain
Lower back pain affects millions of people worldwide. It impacts daily activities and quality of life. Understanding its nature and causes is crucial for effective management.
Common Causes
Lower back pain typically stems from mechanical issues related to movement. Poor posture, prolonged sitting, and improper lifting techniques often trigger discomfort. Muscle strains, ligament sprains, and herniated discs are frequent culprits behind acute pain episodes.
Physical factors like obesity and lack of exercise can contribute to persistent back problems. Additionally, workplace ergonomics and daily movement patterns play significant roles in preventing or exacerbating back pain.
Identifying Symptoms
Recognizing the type of pain helps determine appropriate treatment. Sharp, shooting pain might indicate nerve involvement. Dull, constant aches often suggest muscle strain.
Pain patterns vary. Some experience morning stiffness that improves with movement. Others feel worse as the day progresses. The location and intensity of pain can provide valuable clues about its underlying cause.
Watch for red flags like numbness, tingling, or weakness in the legs. These symptoms may signal more serious conditions requiring immediate medical attention.
Key Takeaway: Lower back pain commonly results from mechanical issues and poor movement patterns. Symptoms vary from sharp to dull aches. Understanding these patterns is essential for effective treatment.
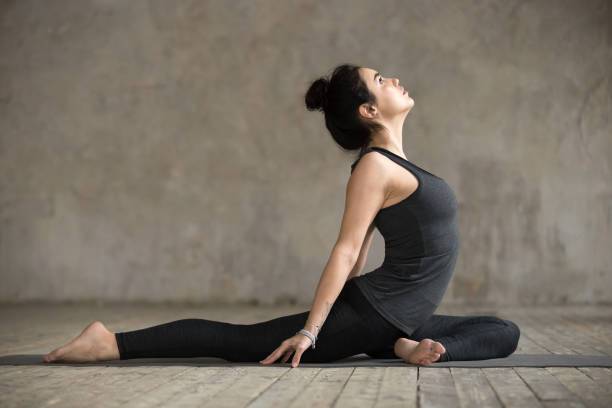
Essential Stretching Exercises
Cat-Cow Stretch
Start your stretching routine with the gentle Cat-Cow movement. Position yourself on your hands and knees. Ensure your wrists align beneath your shoulders and knees under your hips. As you inhale, arch your back, lifting your chest and tailbone toward the ceiling (Cow pose). Then exhale, rounding your spine upward while tucking your chin to your chest (Cat pose).
Perform this movement slowly for 8-10 repetitions. This dynamic stretch improves spinal mobility and relieves tension in your lower back muscles.
Child’s Pose
After warming up with Cat-Cow, transition into Child’s Pose. Kneel on the floor with your big toes touching and knees hip-width apart. Sit back on your heels and extend your arms forward, lowering your chest toward the ground. Hold this position for 30-60 seconds while taking deep breaths.
This restorative pose gently stretches your lower back muscles and provides immediate relief. If you experience knee pain, place a cushion between your thighs and calves.
Knee-to-Chest Stretch
Lie on your back with both knees bent and feet flat on the floor. Slowly bring one knee toward your chest, holding it with both hands. Keep your lower back pressed against the floor and hold for 20-30 seconds. Release and repeat with the other leg.
This stretch targets your lower back and hip muscles effectively. For a deeper stretch, you can bring both knees to your chest simultaneously, but only if it doesn’t cause discomfort.
Piriformis Stretch
While still on your back, cross your right ankle over your left knee, creating a figure-4 position. Gently pull your left thigh toward your chest, maintaining a flat back. Hold for 20-30 seconds and switch sides.
This stretch helps relieve sciatic nerve pressure and loosens tight hip muscles that can contribute to lower back pain.
Key Takeaway: Regular practice of these essential stretches can significantly improve lower back flexibility and reduce pain. Focus on gentle movements that target key muscle groups while maintaining proper form.
Core Strengthening Exercises
Core strength plays a vital role in supporting your lower back and maintaining proper posture. A strong core acts as a natural brace, reducing strain on your spine during daily activities.
Bridge Exercise
The bridge exercise effectively targets your core muscles while being gentle on your spine. Start by lying on your back with knees bent and feet flat on the floor. Keep your arms at your sides, palms down. Slowly lift your hips off the ground until your body forms a straight line from shoulders to knees. Hold this position for 5-10 seconds, then lower back down. Perform 10-12 repetitions.
Bird Dog
This exercise enhances core stability while improving balance. Begin on your hands and knees in a tabletop position. Simultaneously extend your right arm forward and left leg backward until both are parallel to the floor. Maintain a neutral spine and avoid rotating your hips. Hold for 5 seconds, then return to the starting position. Alternate sides and complete 8-10 repetitions per side.
Remember to breathe steadily throughout these exercises and stop if you experience any sharp pain. Start with fewer repetitions and gradually increase as your strength improves.
Key Takeaway: Regular practice of core strengthening exercises like bridges and bird dogs helps stabilize your spine, improve posture, and reduce lower back pain through controlled, gentle movements.
Side-Specific Pain Management
Managing side-specific lower back pain requires a targeted approach. When pain occurs on one side, it often indicates specific muscle involvement or nerve compression that needs careful attention.
Understanding Unilateral Back Pain
One-sided back pain commonly stems from muscle strain, herniated discs, or sciatica affecting a particular side. This localized discomfort can range from a dull ache to sharp, shooting pain that may extend down one leg.
Targeted Relief Strategies
For right-sided pain, focus on gentle stretches that target the affected area while maintaining proper spinal alignment. Left-sided discomfort often responds well to controlled rotational movements that help decompress the affected nerves and muscles.
Position-Specific Techniques
When experiencing side-specific pain, try lying on the non-affected side with a pillow between your knees. This position helps reduce pressure on the painful area while promoting proper spinal alignment. You can also perform gentle stretches while maintaining this position to gradually increase mobility.
Professional Intervention
If side-specific pain persists beyond a few days or worsens with movement, consult a healthcare provider. They can determine the exact cause and recommend targeted treatments, which might include specific exercises or manual therapy techniques.
Key Takeaway: Side-specific back pain requires targeted relief strategies and proper positioning techniques. Persistent unilateral pain should be evaluated by a healthcare professional for appropriate treatment.
Daily Activity Modifications
Proper Posture During Daily Tasks
Maintaining correct posture during everyday activities is crucial for managing lower back pain. When sitting, keep your feet flat on the floor. Use a lumbar support pillow to maintain the natural curve of your spine. While standing, distribute your weight evenly between both feet and avoid prolonged periods in one position.
When lifting objects, remember to bend at your knees rather than your waist. Keep the object close to your body and avoid twisting movements. If you need to turn, pivot your entire body instead of just your torso.
Workplace Ergonomics
Your workspace setup plays a vital role in preventing back strain. Position your computer monitor at eye level. Keep your keyboard and mouse within easy reach. Use an ergonomic chair that supports your lower back and allows your feet to rest comfortably on the floor.
Take regular breaks every 30-45 minutes to stand up, stretch, and walk around. This helps prevent muscle stiffness and promotes better blood circulation. Consider using a standing desk for part of your workday to alternate between sitting and standing positions.
For those who spend long hours on the phone, use a headset instead of cradling the phone between your ear and shoulder. This simple change can prevent unnecessary neck and upper back strain that often leads to lower back issues.
Key Takeaway: Implement proper posture habits and ergonomic adjustments in your daily activities. This minimizes back strain and supports your spine’s natural alignment during work and routine tasks.
Recovery and Rehabilitation
The Role of Physical Therapy
Physical therapy plays a crucial role in recovering from lower back pain. A qualified physical therapist can design a personalized rehabilitation program. This program addresses your specific condition and pain levels. They use various techniques, including manual therapy, targeted exercises, and movement education. These help restore function and prevent future injuries.
During your sessions, therapists will monitor your progress and adjust exercises based on your response. They’ll also teach you proper body mechanics and movement patterns to protect your back during daily activities.
Progressive Exercise Implementation
Recovery from lower back pain requires a gradual approach to exercise. Start with gentle movements and basic stretches. Then progress to more challenging exercises as your strength and mobility improve. This step-by-step progression helps prevent re-injury while building the necessary strength and flexibility.
Begin with low-impact activities like walking or swimming for 15-20 minutes daily. As your pain decreases, incorporate specific strengthening exercises targeting your core and back muscles.
Remember to listen to your body and avoid pushing through sharp or increasing pain. Consistency is key in rehabilitation. Perform your prescribed exercises regularly, typically 2-3 times per day. Track your progress and celebrate small improvements along the way.
Key Takeaway: Successful recovery from lower back pain combines professional physical therapy guidance with a consistent, progressive exercise program. This gradually builds strength and mobility while preventing re-injury.
Prevention Strategies
Maintain Good Posture
Maintaining proper posture is crucial for preventing lower back pain. Keep your shoulders back, chin tucked, and spine aligned whether sitting or standing. When sitting, use a chair with good lumbar support. Keep your feet flat on the floor. Take regular breaks every 30-45 minutes to stand up and move around.
Regular Exercise Routine
Incorporating regular physical activity into your daily routine significantly reduces the risk of developing lower back issues. Focus on exercises that strengthen your core muscles, including planks, bridges, and bird dogs. Aim for at least 30 minutes of moderate exercise most days of the week.
Low-impact activities like swimming, walking, or cycling are excellent choices for maintaining back health. These activities improve circulation, strengthen supporting muscles, and maintain flexibility without putting excessive strain on your spine.
Remember to warm up before any exercise session and cool down afterward. This helps prepare your muscles for activity and prevents strain or injury. Start slowly and gradually increase intensity as your strength and endurance improve.
Key Takeaway: Prevent lower back pain by maintaining proper posture throughout the day. Engage in regular, low-impact exercise that strengthens core muscles and promotes flexibility.
Conclusion
Taking control of your lower back pain is a journey that begins with these proven exercises and stretches. By incorporating these rehabilitation techniques into your daily routine, you can significantly improve your mobility. You can reduce discomfort and strengthen your core muscles for long-term relief.
Remember to start slowly and listen to your body throughout the process. While these exercises are effective for most people, consult a physical therapist or healthcare provider if you experience persistent discomfort or have specific medical conditions. Your path to recovery is within reach, and consistency is key.
Begin with gentle stretches and gradually progress to more challenging exercises as your strength improves. By maintaining proper form and following this comprehensive exercise program, you’re not just treating your current pain. You’re building a stronger foundation for a pain-free future.
Take the first step today and commit to your back health journey.
FAQs
How long should I hold each lower back stretch for optimal results?
Hold each stretch for 15-30 seconds, repeating 3-5 times per session. Avoid bouncing or forcing the stretch. Listen to your body and maintain steady breathing throughout the movement. For beginners, start with shorter durations and gradually increase as comfort improves.
Can I do lower back exercises if I have a herniated disc?
Always consult your physical therapist or orthopedic surgeon before starting any exercise program with a herniated disc. Some gentle stretches may help, but others could worsen your condition. A customized routine based on your specific condition is essential for safe recovery.
Is it normal to feel some discomfort during lower back exercises?
Mild discomfort during exercises is normal, but you should never experience sharp or intense pain. If you experience ongoing back pain or intense muscle spasms, stop immediately and seek medical attention. The right kind of exercise should feel challenging but manageable.
How often should I perform lower back exercises for the best results?
Perform these exercises 2-3 times daily, starting with a routine of simple stretches. As your back strength improves, gradually increase frequency and intensity. Consistency is key for maintaining spinal health and preventing future back problems.
Should I apply heat or ice after lower back exercises?
Apply heat before exercises to warm up muscles and improve flexibility. After exercises, use ice if there’s any inflammation or discomfort. Each application should last 15-20 minutes. For chronic lower back pain, alternate between heat and ice based on what provides more relief.
Can a sedentary lifestyle contribute to lower back pain?
Yes, a sedentary lifestyle significantly contributes to lower back pain through weakened abdominal muscles and poor posture. Regular movement, proper stretching, and incorporating everyday activity into your workday can help prevent back problems associated with prolonged sitting.




![The Ultimate Guide to Increasing Flexibility: 10 Simple At-Home Exercises [With Videos]](https://bodyamigo.com/wp-content/uploads/2025/01/pexels-photo-3757955-440x293.webp)
![The Ultimate Guide to Increasing Flexibility: 10 Simple At-Home Exercises [With Videos]](https://bodyamigo.com/wp-content/uploads/2025/01/pexels-photo-3757955-320x213.webp)


Leave a Comment